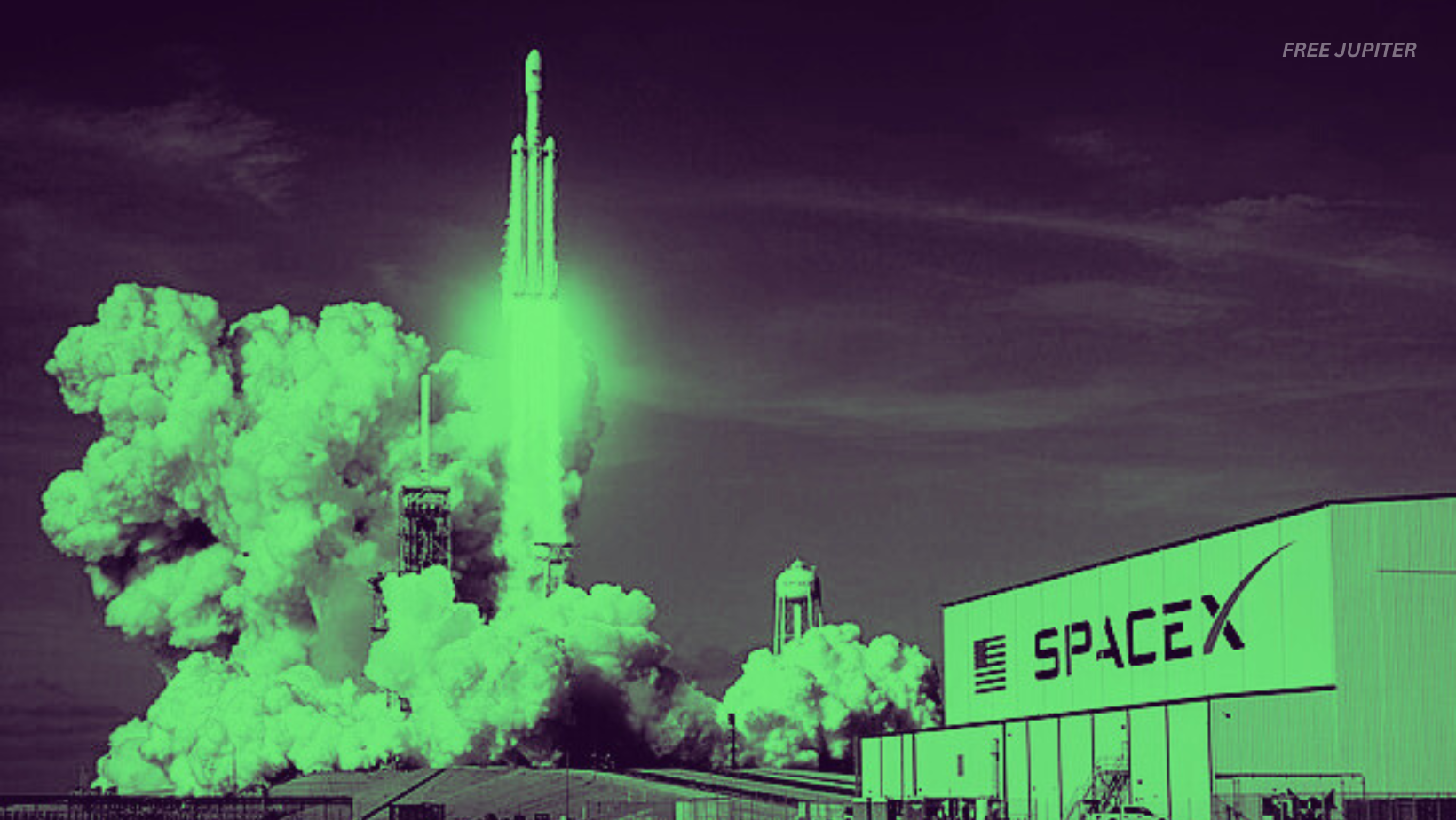
Just weeks after a previous test flight ended in a dramatic mid-air explosion, SpaceX launched another massive Starship rocket on Thursday. However, the mission was cut short when contact was lost with the spacecraft, which then tumbled and broke apart in the sky.
This time, debris from the incident was spotted falling over Florida. It remained unclear whether the spacecraft’s self-destruct mechanism had activated to destroy it. The 403-foot rocket had lifted off from Texas, and its first-stage booster successfully landed back at the launch site with the help of enormous mechanical arms. However, as the upper-stage spacecraft continued on its journey, its engines began shutting down one by one. The planned trajectory was supposed to take it over the Indian Ocean for a controlled descent, but the vehicle instead spiraled out of control before contact was lost.
Before the failure, Starship had climbed nearly 90 miles above the Earth’s surface. It was expected to deploy four mock satellites, but the malfunction prevented that step from happening. The exact location of where the wreckage fell was not immediately known, though videos circulating online captured images of fiery debris falling over Florida, including near Cape Canaveral.
The test flight had been planned to last approximately an hour.
“Unfortunately, we’ve been here before,” remarked SpaceX flight commentator Dan Huot. “We’ve had practice with this.”
SpaceX later confirmed in a statement that the vehicle had experienced what the company referred to as a “rapid unscheduled disassembly” during the ascent phase. The team quickly initiated coordination with safety authorities to implement pre-established contingency plans.
This test flight did not reach the same altitude or travel as far as the previous attempt.
NASA has already committed to using Starship for upcoming lunar missions, with plans to land astronauts on the Moon within the next few years. Meanwhile, SpaceX founder Elon Musk envisions Starship as the key to reaching Mars, making it the most powerful rocket ever developed.
As with previous test flights, this mission carried simulated payloads designed to mimic the Starlink satellites that SpaceX has deployed in low Earth orbit. These test units were meant to fall back to Earth shortly after reaching space, but the flight’s failure prevented their release.
Ahead of this launch, several modifications had been made to the spacecraft. Changes were focused on improving its aerodynamic flaps, onboard computers, and fuel systems. The ultimate goal was to perfect the ability to return the upper stage of the rocket back to the launch site, mirroring the recovery of the booster.
During a prior test, the booster had successfully made it back to the launch pad, but the upper-stage vehicle exploded minutes later over the Atlantic Ocean. There were no reports of injuries or significant damage from that incident.
Investigations into that failure suggested that leaking fuel had caused a series of fires, leading to an engine shutdown. The onboard self-destruct mechanism was then activated as a safety measure. In response, SpaceX implemented various design improvements, and after thorough assessments, the Federal Aviation Administration granted clearance for another test launch.
Starship flights originate from SpaceX’s private launch site in southern Texas, near the Mexican border. Additionally, the company is constructing another Starship launch complex at Cape Canaveral, Florida, where its Falcon rockets already carry astronauts and satellites into orbit.
Despite repeated setbacks, SpaceX remains determined to push forward with the development of Starship. Each test, whether a success or a failure, provides crucial data that moves the company closer to achieving its long-term ambitions in space exploration.
The Bigger Picture: Why Starship Matters
The repeated failures of Starship’s test flights have not discouraged SpaceX’s pursuit of its ultimate goal—interplanetary travel. Designed to be fully reusable, Starship represents a significant shift in the approach to space travel. Unlike traditional rockets that are discarded after a single use, this spacecraft aims to drastically reduce the cost of space exploration by enabling multiple flights with the same hardware.
The long-term vision involves using Starship for crewed missions to Mars, as well as commercial space travel, cargo deliveries, and even space tourism. The ability to carry large payloads and transport passengers efficiently has been viewed as a game-changer in the aerospace industry.
NASA has also placed considerable faith in the program. The agency has contracted SpaceX to use Starship as a lunar lander for its Artemis program, which aims to return humans to the Moon for the first time since the Apollo missions. The spacecraft’s ability to carry astronauts and supplies plays a crucial role in NASA’s plans for a sustained lunar presence.
Challenges in Starship’s Development
The road to making Starship a reality has been filled with technical hurdles. Engine reliability remains a significant concern, as test flights have frequently experienced unexpected shutdowns. Fuel system leaks have also been a persistent issue, leading to onboard fires and system failures. Engineers have been continuously tweaking the design, but each test flight exposes new challenges that must be addressed before the spacecraft can be deemed flight-ready for human missions.
In addition to technical difficulties, regulatory and environmental factors have slowed progress. Each launch requires approval from the Federal Aviation Administration, which must assess the risks posed to public safety and the environment. SpaceX’s launch facility in Texas has also been the subject of environmental scrutiny, with concerns raised over the impact of frequent rocket tests on local wildlife and ecosystems.
The Future of Starship
Despite the setbacks, progress continues to be made. SpaceX has been steadily refining its designs, incorporating lessons from previous failures into each new iteration. Plans for the next test flight are already underway, with additional modifications expected to be implemented before the next attempt.
In the long run, SpaceX envisions a future where Starship plays a critical role in enabling space colonization. Musk has repeatedly stated his ambition to make life “multi-planetary,” with Mars as the ultimate target. The success of Starship is seen as a necessary step toward that goal.
As test flights continue, each failure brings new insights that inch the company closer to success. While the dream of reaching Mars remains distant, the rapid pace of development suggests that Starship may one day revolutionize space travel, paving the way for a future where space is more accessible than ever before.
For now, the challenges remain formidable, but the progress is undeniable. With each launch, SpaceX moves closer to making its ambitious vision a reality. Whether Starship’s next test flight ends in success or another fiery explosion, one thing is certain—the journey to the stars is far from over.