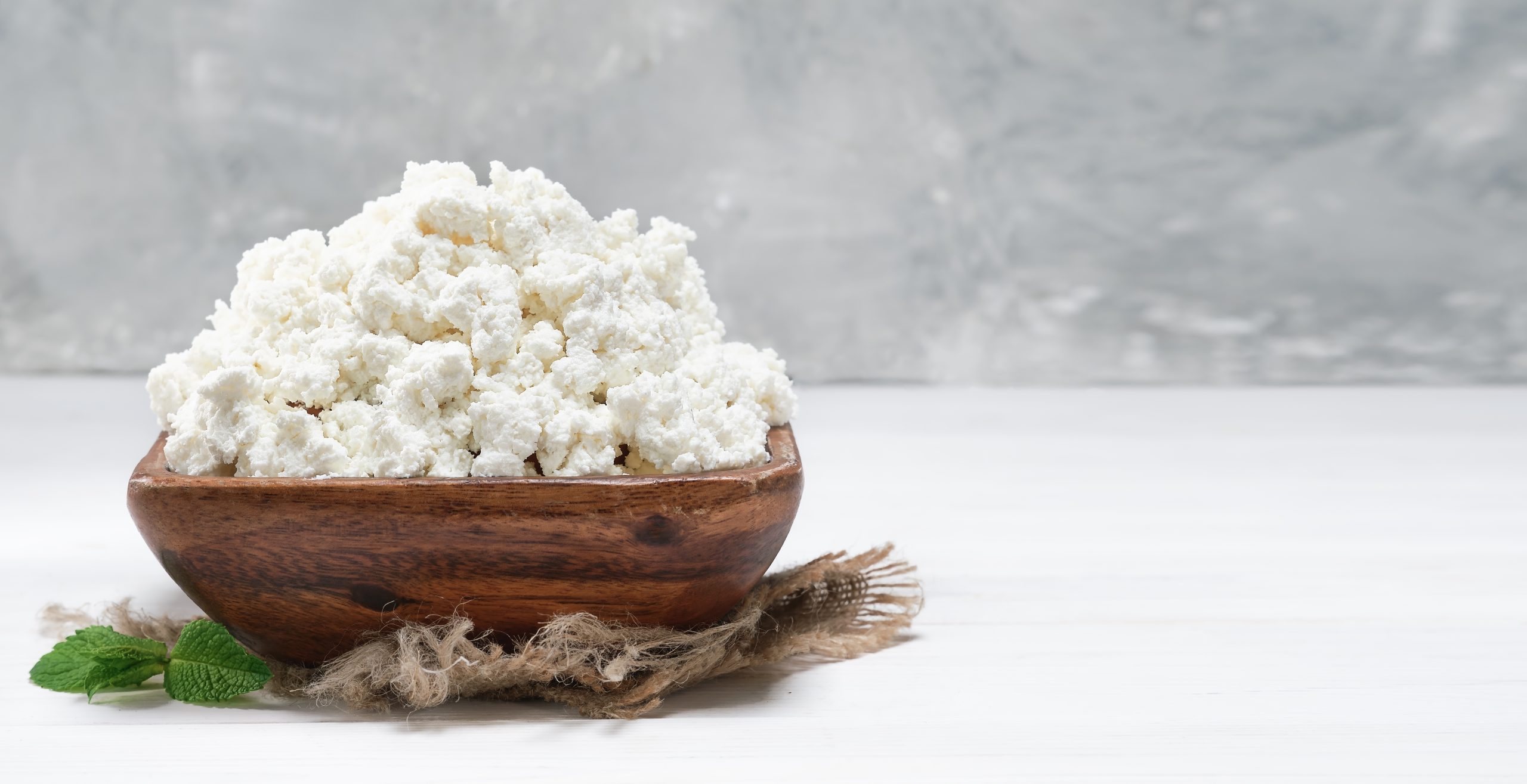
Cottage cheese is a nutrient-dense dairy product that has gained popularity due to its high protein content. It is a staple in many breakfast meals, particularly among those who engage in morning workouts. Its slow-digesting protein makes it a great post-exercise snack, helping with muscle recovery and satiety. Additionally, it serves as a wholesome option for curbing hunger between meals, making it an excellent addition to a balanced diet. With its soft, lumpy texture and mild, slightly tangy flavor, cottage cheese is not only versatile but also loaded with essential nutrients that support overall health and well-being.
Nutritional Value of Cottage Cheese
A single cup of creamed cottage cheese provides:
- Calories: 206 kcal
- Fat: 9.03 grams
- Protein: 23.3 grams (46.6% of daily recommended intake)
- Carbohydrates: 7.1 grams
- Sugars: 5.61 grams
- Calcium: 174 mg (13.4% DV)
- Iron: 0.147 mg (0.8% DV)
- Magnesium: 16.8 mg (4% DV)
- Potassium: 218 mg (4.6% DV)
- Sodium: 662 mg
- Zinc: 0.84 mg (7.6% DV)
For those opting for a lower-fat version with 3% milk fat, the nutritional values slightly differ:
- Calories: 189 kcal
- Fat: 5.06 grams
- Protein: 24.2 grams (48.4% DV)
- Carbohydrates: 9.48 grams
- Sugars: 9.02 grams
- Calcium: 227 mg (17.46% DV)
- Iron: 0.286 mg (1.59% DV)
- Magnesium: 19.6 mg (4.67% DV)
- Potassium: 264 mg (5.62% DV)
- Sodium: 706 mg
- Zinc: 1.34 mg (12.18% DV)
While nonfat varieties exist, they may not provide the same level of satiety due to their reduced protein and fat content.
Supports Muscle Growth
One of the most well-known benefits of cottage cheese is its high casein protein content. Casein is a slow-digesting protein that contains essential amino acids necessary for muscle repair and growth. These amino acids also play a role in appetite regulation, energy balance, and metabolic function, making cottage cheese an excellent dietary choice for those looking to maintain or build muscle mass. Additionally, its high leucine content helps stimulate muscle protein synthesis, which is essential for recovery after workouts.
Promotes Bone Health
Beyond muscle maintenance, the protein in cottage cheese contributes to the strength of other tissues, including bones. Cottage cheese is rich in calcium and phosphorus—two minerals essential for bone formation and the prevention of osteoporosis. These minerals work together to maintain bone density and structural integrity, reducing the risk of fractures and bone loss as the body ages. Regular consumption can support long-term skeletal health, especially for individuals at risk of osteoporosis.
Aids in Weight Management
Due to its high protein content and slow digestion rate, cottage cheese helps promote fullness, reducing the likelihood of overeating. Casein protein takes longer to break down, leading to prolonged satiety, which may support weight management by limiting excess calorie intake and preventing unnecessary snacking throughout the day. Additionally, its relatively low-calorie content makes it an ideal choice for those looking to control their weight without compromising on essential nutrients.
Supports Digestive Health
The fermentation process involved in making cottage cheese introduces beneficial bacteria, which may aid in gut health. Some brands also include probiotics—live microorganisms that help balance the digestive system and support healthy gut flora. A well-balanced gut microbiome is crucial for efficient digestion, improved immune function, and reduced inflammation. If probiotics are a priority, it is important to check product labels for terms such as “live and active cultures.”
Enhances Nervous System Function
Cottage cheese is an excellent source of B vitamins, particularly vitamin B12 and riboflavin. Vitamin B12 plays a crucial role in nervous system function, DNA synthesis, and red blood cell production. A deficiency in B12 can lead to neurological issues, fatigue, and cognitive decline. Meanwhile, riboflavin helps protect nerve cells by reducing oxidative stress and inflammation. Including cottage cheese in the diet can contribute to better cognitive function and overall neurological health.
May Lower Cancer Risk
Research suggests that dairy consumption, including cottage cheese, may be linked to a reduced risk of certain cancers. The calcium found in dairy products has been associated with lower risks of gastric, bladder, breast, and colorectal cancers. Calcium is believed to regulate cell growth and differentiation, which may help prevent abnormal cell development. While more studies are needed, incorporating dairy into a balanced diet appears to have protective health benefits.
Potential Concerns
Despite its numerous advantages, cottage cheese does have a relatively high sodium content. While sodium is essential for bodily functions, excessive intake can contribute to high blood pressure. Many processed and packaged foods already contain high levels of sodium, so individuals monitoring their intake should consider low-sodium cottage cheese alternatives.
Additionally, since it is a dairy-based product, cottage cheese may not be suitable for individuals with lactose intolerance. Symptoms such as bloating, gas, and stomach discomfort may occur in those who have difficulty digesting lactose.
Ways to Enjoy Cottage Cheese
Cottage cheese can be eaten plain or paired with a variety of ingredients to enhance its flavor. Below are some creative ways to incorporate it into meals:
Sweet Options:
- Fresh fruit (berries, sliced bananas, or chopped apples)
- Nuts and seeds for added crunch
- Spices like cinnamon or nutmeg
- A drizzle of honey or maple syrup for natural sweetness
Savory Combinations:
- Diced tomatoes and cucumbers with olive oil and fresh herbs
- Salt, pepper, and leafy greens
- Mixed with salsa to create a flavorful dip
For those who dislike its texture, blending cottage cheese until smooth creates a consistency similar to yogurt, making it easier to enjoy in different ways.
Additional Ways to Incorporate Cottage Cheese
- Add to scrambled eggs for extra protein
- Blend into pasta sauces for a creamy consistency
- Substitute for ricotta in lasagna
- Mix with seasonings for a flavorful vegetable dip
- Blend into smoothies for a protein boost
- Spread on toast or avocado toast
- Toss into fresh salads
- Use as a filling in breakfast burritos
- Stir into quiches or casseroles
- Spoon over baked potatoes
- Mix with grains like rice or quinoa
- Incorporate into pancake or waffle batter
Conclusion
Cottage cheese is a nutrient-dense and highly versatile food that offers a range of health benefits, from muscle support and bone strength to digestive health and weight management. While its sodium content may be a concern for some individuals, choosing lower-sodium options can help mitigate this issue. Whether enjoyed in sweet or savory dishes, cottage cheese is an excellent addition to a healthy diet, providing essential nutrients and satisfying taste in a variety of ways.